Blog
Vim is a powerful text editor, but its multiple modes can be intimidating. Here’s how to use it to save files.
Vim is one of the most powerful and popular command-line text editors on Linux, but it can also be a little intimidating. With its multiple modes and sometimes unintuitive commands, it’s easy to get lost starting out. One particular struggle for new Vim users is knowing how to save a file.
How to Save a file in Vim
Without too much preamble, the command to save in Vim is :w. However, you may have noticed that if you just type this into your document nothing happens. This is because to use a command in Vim, you first have a switch to “normal mode”, which will allow you to run commands. So, full process looks like this:
- Press
Escon your keyboard to enter normal mode. - Type
:w. - Press
Enterto run the command.
How to Save As in Vim
As with most text editors, Vim also has a “Save As” function, allowing you to write the changes you made to a document to a separate file. To use it, follow these steps:
- Press
Escto enter normal mode. - type
:w yourfilename.txt. - Press
Enter.
How to save and quit in Vim
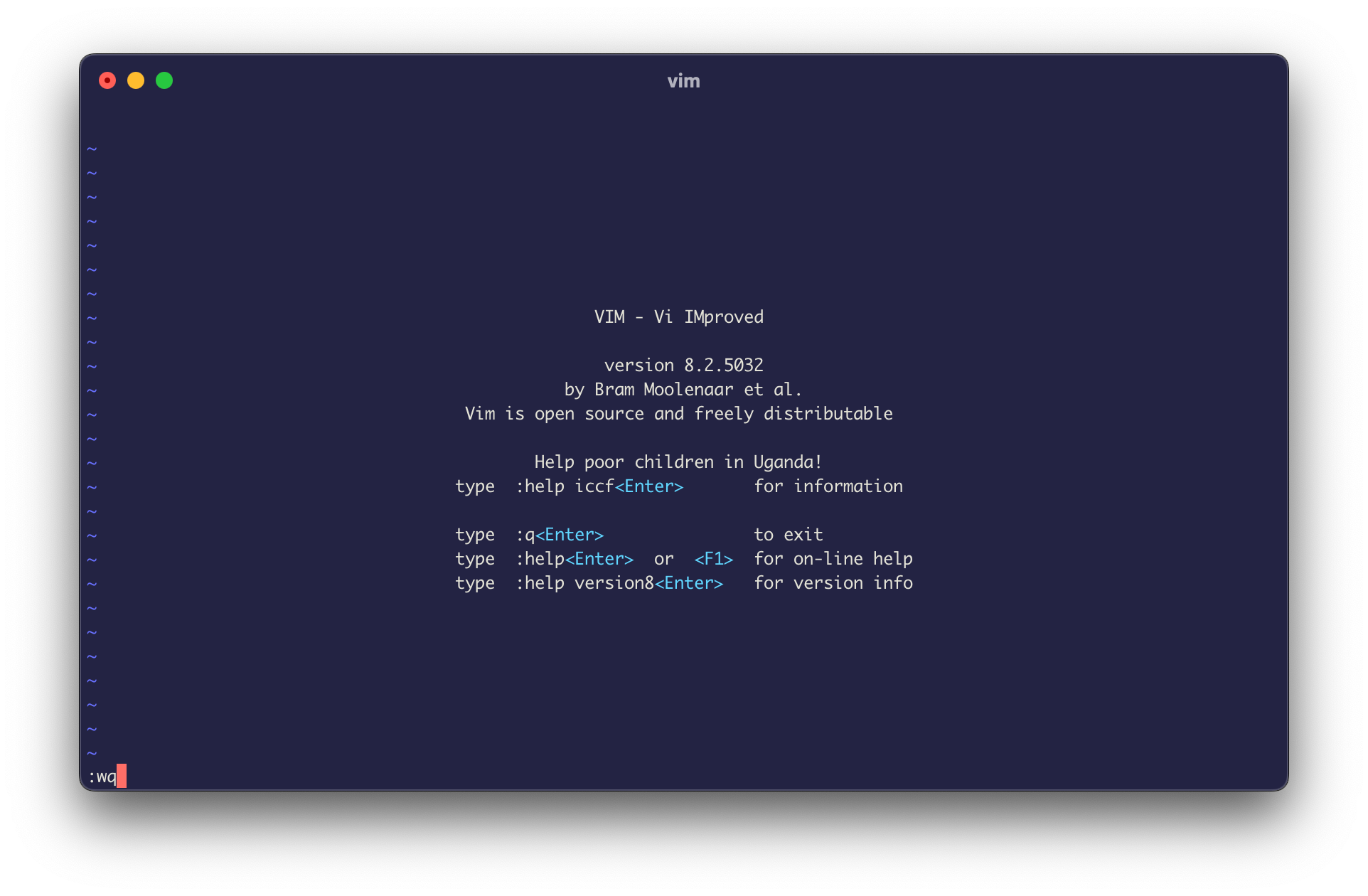
To save yourself some time, you can save and quit in a single command. Just use :wq instead of :w:
- Press
Esc. - Type
:wqor:wq filename.txt. - Press
Enter.
Alternatively, you can use the :x command. This will only save the file if there are unsaved changes, whereas :wq will always save and update the modification time in the file’s metadata.
Exit Vim without saving
The final scenario that you might run into is the need to quit a file in Vim without saving at all. If :w writes and :wq writes and quits, it should obvious that :q stands for quit. However, Vim will not let you quit using this command if you have unsaved changes to a file. Instead, you’ll have to follow these steps:
- Press
Esc - Type
:q! - Press
Enter
The ! forces Vim to quit even if there are unsaved changes to the file.
